Have you ever touched something and noticed your skin becoming red and itchy? This reaction could be contact dermatitis. Your skin is like a shield, protecting you from harm. When something harmful touches it, your skin reacts. In the case of what causes contact dermatitis, your immune system overreacts to the allergen or gets damaged by the irritant, leading to the rash symptoms.
Contact dermatitis is a common skin condition that falls under eczema and dermatitis. It affects 9% of the UK population and is the most common type of work-related skin condition. This condition is seen across all ages and backgrounds, making it a widespread skin issue.
There are two main types of contact dermatitis:
Unlike other skin problems, contact dermatitis is not caused by hormones or viruses inside your body; it is caused by external factors. It usually only affects the skin area that touches the irritant or allergen.
Some people are more likely to get contact dermatitis than others. This can depend on several factors:
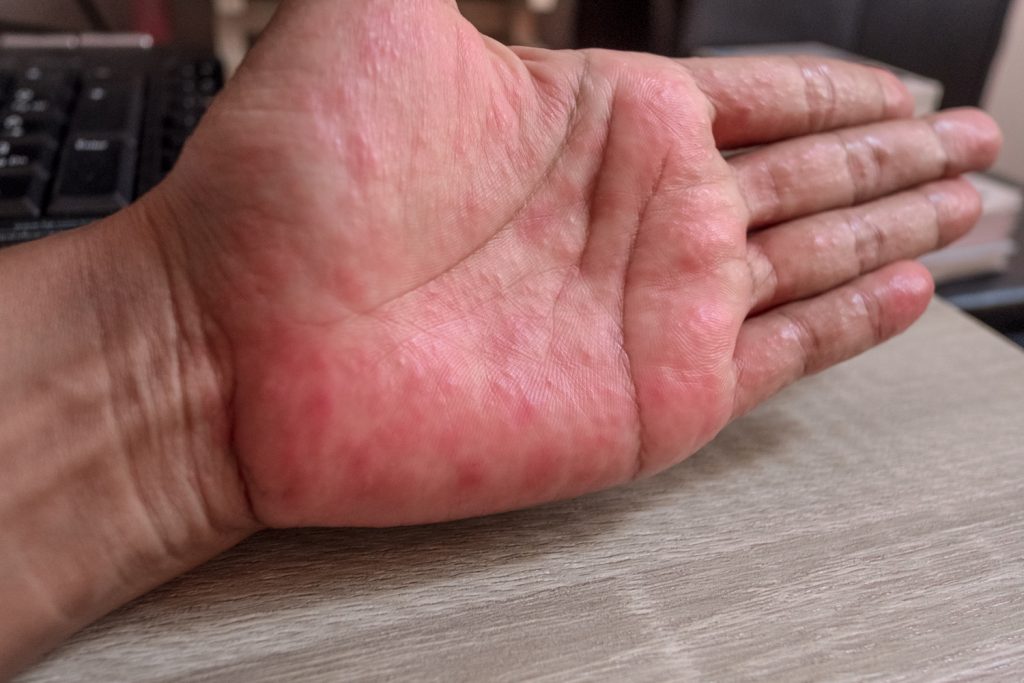
Contact dermatitis can cause several noticeable changes to your skin:
The symptoms of contact dermatitis usually appear on the part of your body that touches the allergens and irritants. Common areas include:
Remember, the location of the rash can give you clues about what caused it. For example, a rash on your wrist might be due to a watch or bracelet.
Contact dermatitis happens when your skin reacts to certain substances. These can be things you touch every day or rare items.
When something your body doesn’t like touches your skin, your immune system responds. If you see your skin swell or become inflamed, it’s a sign your white blood cells are reacting to the allergen or irritant. This can lead to an itchy rash. The rash might show up in minutes with an irritant or take hours or days after exposure to an allergen.
Allergic contact dermatitis occurs when your immune system reacts to contact with an allergen. Here, your body mistakenly sees a harmless substance as a threat and responds to protect you:
When these allergens touch your skin, your immune system releases chemicals. This causes the skin to become itchy and inflamed.
Only sometimes. The rash takes a few days to appear after contact with the allergen, and each person’s reaction time can vary.
Irritant contact dermatitis is different from the allergic type. It’s caused by direct damage to your skin from a substance:
When these irritants touch your skin, they can damage its outer layer. This leads to irritation and a rash. Unlike allergic contact dermatitis, this type doesn’t involve your immune system.
Figuring out if you have contact dermatitis involves a few steps. Doctors, like GPs or dermatologists, play a significant role in this.
The treatment for irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis is the same. There are two main differences in treatment:
Emollients are treatments used for managing conditions like eczema and dermatitis, as they moisturise the skin and form a protective layer. There are various types, and finding the right one may involve trial and error. Options include:
Creams and lotions are less greasy, making them suitable for daytime use, while ointments are better for very dry areas and night use. If an emollient stops working or irritates your skin, consult your pharmacist for alternatives.
More intensive treatment might be needed during a severe contact dermatitis outbreak, where your skin is sore and inflamed.
Your GP or pharmacist can prescribe a topical corticosteroid as a cream or ointment for direct application to reduce inflammation. Mild steroid creams are also available for smaller affected areas.
The prescribed corticosteroid’s strength varies based on your dermatitis severity and the skin area. Prescriptions may include:
Always follow the instructions in the patient information leaflet accompanying your medication.
Preventing contact dermatitis involves a few important steps:
At Click2Pharmacy, we offer a variety of treatments for contact dermatitis. Our range includes creams, moisturisers, and medications, both over-the-counter and prescribed by healthcare professionals. We understand the discomfort of contact dermatitis and strive to provide effective solutions. Visit our online Eczema and Dermatitis clinic for a selection that suits your specific needs, and enjoy the convenience of having your treatment delivered directly to you. We are committed to helping you manage your contact dermatitis effectively and comfortably.
Contact dermatitis and eczema are both skin conditions, but they are different:
Contact dermatitis isn’t contagious. You cannot catch it from someone else. It’s caused by your skin’s reaction to certain substances, not by a virus or bacteria that can be passed on. This misconception might come from seeing similar rashes on different people, especially if they’ve been in contact with the same irritant or allergen. If you’re around someone with contact dermatitis, you don’t need to worry about catching it. However, if you touch the same substance that caused their rash, you might experience symptoms of contact dermatitis if you’re sensitive to it.







